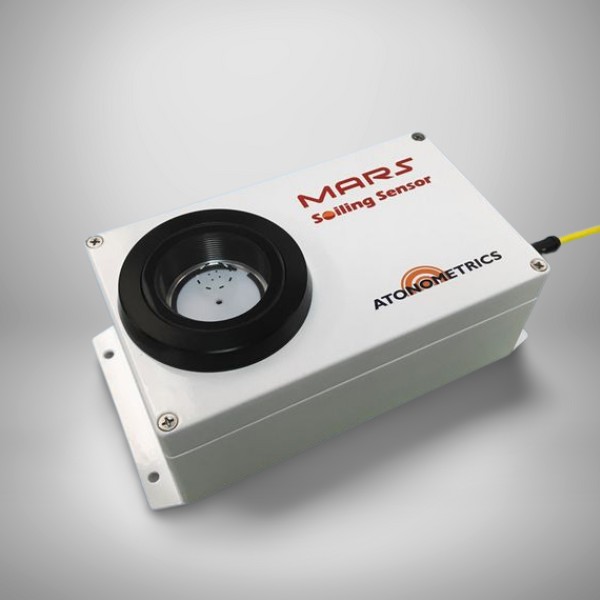
Mars Soiling Sensor:
A Mars Soiling Sensor is a device used to detect and measure the amount of dust and debris that accumulates on the surface of Mars. This is important for several reasons. First, dust and debris can accumulate on solar panels and other surfaces, reducing their efficiency and lifespan. Dust also accumulates on lenses and other optical surfaces, reducing visibility and making it difficult to take clear images. Additionally, dust storms on Mars can be severe, and an understanding of how they affect the planet’s atmosphere and weather patterns can help scientists to better understand the planet’s overall climate.
The sensors typically consist of a light source and a detector that are used to measure the amount of light that is scattered or absorbed by the dust and debris. This data is then used to determine the thickness of the dust and debris layer, as well as the size and shape of the particles. Some of the Mars Soiling Sensor also equipped with thermocouples, which can measure temperature and help to understand the thermal behavior of dust.
These sensors have been used on several missions to Mars, including the Viking landers, the Mars Exploration Rovers, the Phoenix lander, the Mars Science Laboratory, and the In Sight lander. They have provided valuable information about the planet’s dust and debris, helping scientists to better understand its geology, weather, and climate. Future missions to Mars, such as the Mars 2020 mission and the Exo Mars mission, also plan to use soiling sensors to gather data about the planet.
Overall, Soiling sensor plays a vital role in the understanding of the Mars surface and atmosphere, providing crucial information to scientists and engineers for determining mission success, as well as helping to pave the way for future manned missions to the planet.
Application and features of Mars Soiling Sensor:
Application |
Features |
|---|---|
| ✅ Determining accurate soiling losses for PV performance guarantees ✅ Monitoring soiling losses to enable detection of other system-level issues ✅ Optimizing washing schedules for best return-on-investment ✅ Determining typical soiling rates for forecasting models ✅ Collecting pre-construction prospecting data at new sites |
✅ Maintenance-free measurement ✅ No water, washing, or moving parts ✅ Unique all-optical technology ✅ No site-specific calibration required ✅ Ideal for a range of PV plants ✅ Easy installation |